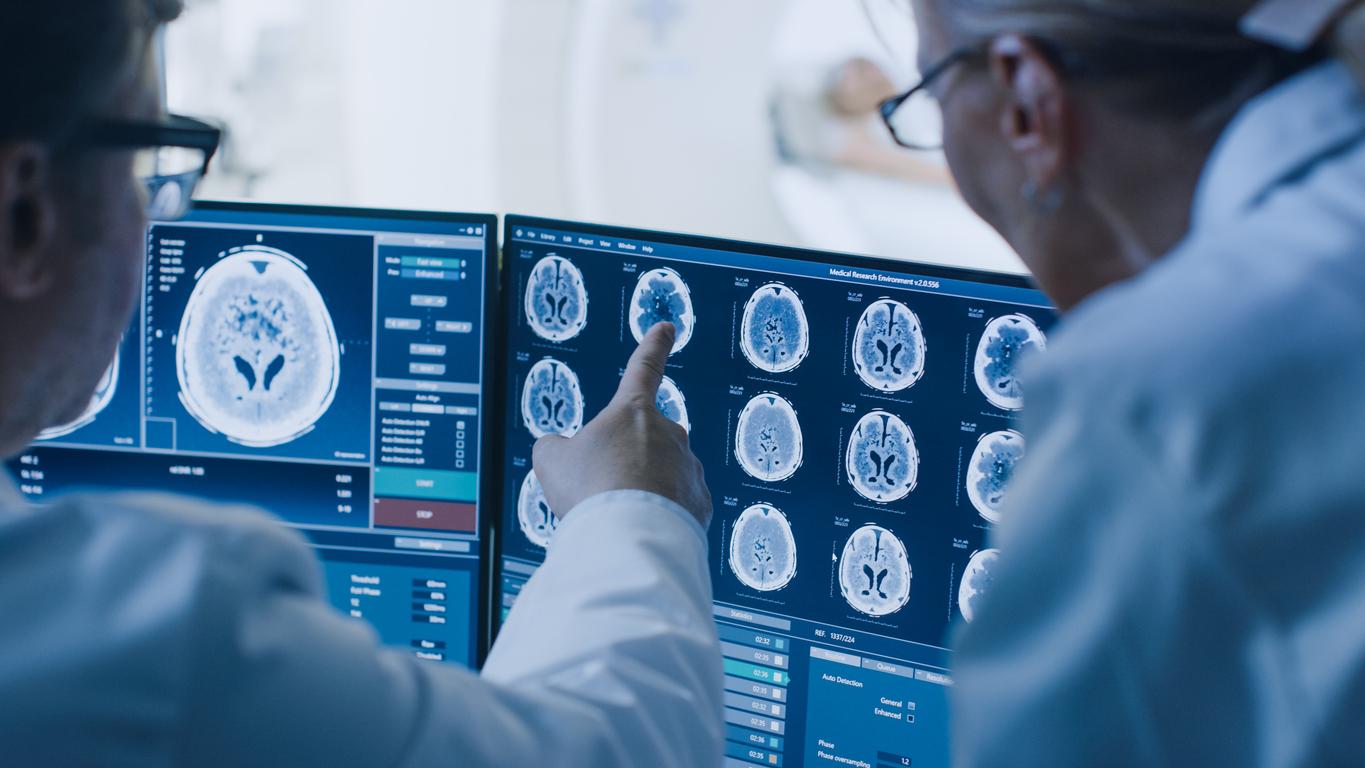
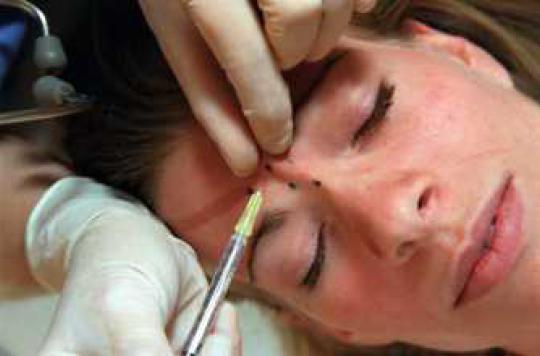
Used to reduce facial wrinkles, botox may reach the central nervous system. This is what an Australian study published in the Journal of Neuroscience concludes.
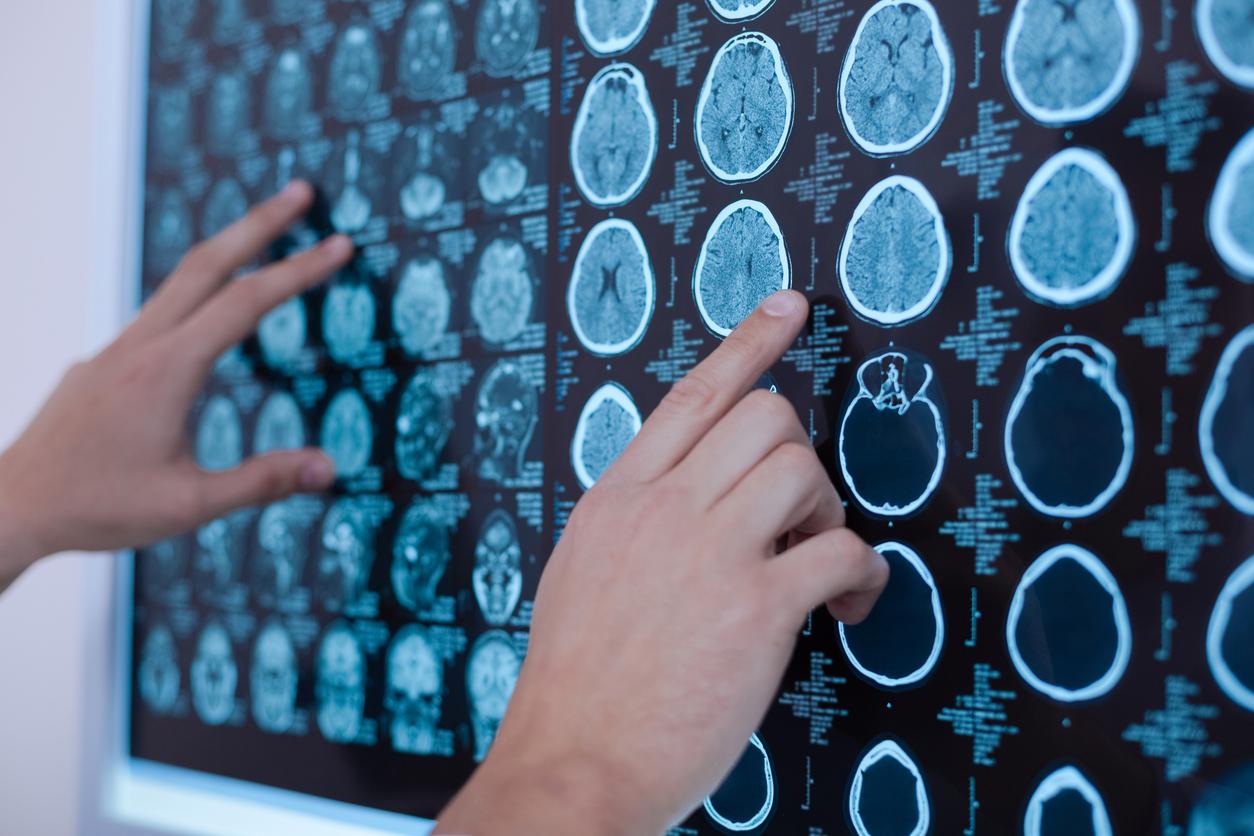
Prized by show biz stars to counter wrinkles, botox would end up making its way into the brain. This is indeed what a team of Australian scientists who have just published a study in The Journal of Neuroscience.
The reassuring scientists
According to this team from the University of Queensland (near Brisbane), botulinum toxin molecules, used by cosmetic surgeons to reduce wrinkles, travel through the nerves, into the brain and spinal cord of patients. To arrive at this observation, they used an advanced microscopy technique to visualize the movements of the toxin molecules up to the central nervous system.
Faced with this discovery, the authors do not want to be alarming, however. Asked by the site Top Health, Frédéric Meunier, co-author of the study confides: “Botox is a safe treatment, which has been used for more than 20 years. It does not cause any side effects, apart from local paralysis, and is a fantastic drug for treating diseases causing overactive muscles. It could all depend on how much toxin is in the nervous system. “
Potentially affected memory
In The Plus of Obs, Jacques Hugon, neurologist and head of service at the Center Mémoire Paris Nord Ile-de-France, believes that if Botox reaches the brain, then other questions arise. “This toxin is known to inhibit the release of acetylcholine, a neurotransmitter that plays an important role in the central nervous system, since it is essential for memory and learning. ”
He adds: “If botulinum toxin entered the brain, it would have the opposite effect, by preventing the” release “of acetylcholine. This could therefore slow down memory capacities and have a detrimental effect on learning capacities. But all this obviously remains to be demonstrated and depends on the dose that would pass into the brain, ”he concludes.
Fewer impulses sent to the brain
This discovery is not the first to show that Botox has effects on the brain. By measuring the electrical activity of the brain before and after an injection of botulinum toxin, researchers from the University of Zurich have shown that the substance also decreases the electrical signals produced by the brain.
The study also shows that botox influencesother areas farther from the injection site, including a region of the brain that controls hand movement. “After injection of the toxin, the sensitivity of the hand was altered”, commented these researchers in an intervention at the Swiss television (rts). Findings that the Botox manufacturing company (Allergan) has always refuted.
As a reminder, Botox is a common product and authorized in France since 2003, doctors and surgeons offer it in the form of renewable injections every 6 months. It reduces wrinkles by causing targeted paralysis of the muscles. Finally, beyond its potentially toxic effects, Botox is an interesting avenue as a treatment for certain pathologies (stomach cancer, urinary insufficiency, migraines).
Source: YouTube video
.